【LLM Review】Decrypt Ptuning - 2023W32
参考论文:P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks
1. 总结
ptuning 是介于prompt engineer和Full FT之间的一种方案,目的是希望用少量训练成本,优化Handcrafted prompt效果,接近Full FT效果,具体效果和model size和task有关,整体看有一定实践价值。
2. ptuning、prompt tuning和prefix tuning的区别
ptuning v1即prompt tuning,prompt virtual token 加入位置不固定且一般为一个token,只在Embedding labyer加 。v2类似prefix tuning ,但部分task去掉了reparameterized,还有一些其他trick,见table1。
- Full FT的问题:While fine-tuning obtains good performance, it is memory-consuming during training because gradients and optimizer states for all parameters must be stored. Moreover, keeping a copy of model parameters for each task during inference is inconvenient since pre-trained models are usually large. (pt的优势:降低训练内存,同时每个task只需存pt部分的trainable variables)
- Fixed Handcraft prompt的问题:discrete prompting (Shin et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2020) can lead to suboptimal performance in many cases compared to fine-tuning. (人类认为合理的prompt不一定对语言模型有效。 其次,手工制定的prompt的微小变化会导致显着的性能差异。)
- 输入Template:
[CLS] I like the Disney films very much. [SEP] It was [MASK]. [SEP] - Verbalizer(label word):具体的分类任务,需要选择指定的标签词(label word)。例如情感分析中,我们期望Verbalizer可能是 V(positive)=great , V(negative)=terrible (positive和negative是类标签)。同样,不同的任务有其相应的label word,但需要注意的是,Verbalizer的构建需要取决于对应的Pattern。因此如何构建Verbalizer是另一个研究挑战。
- 输入Template:
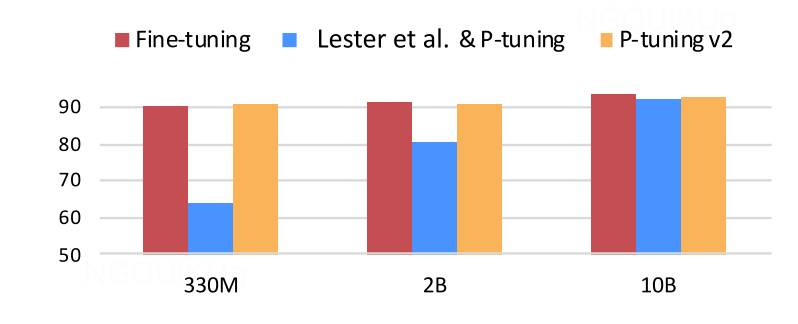
- Prompt Turning(continuous prompts)的问题:While prompt tuning improves over discrete prompt on many tasks, it still underperforms fine-tuning when the model size is not large, specifically less than 10 billion parameters.
- Prefix tuning - Deep prompt tuning:The main difference between prompt tuning and prefix tuning is that prompt tuning only fine-tunes the embedding layer, while prefix tuning fine-tunes all the layers corresponding to the virtual tokens1.
- The most significant improvement originates from appling continuous prompts for every layer of the pretrained model, instead of the mere input layer.
- Performance:Vary depending on the specific task. For example, in Table2Text tasks, prompt tuning with a parameter size of only 0.1% can outperform fine-tuning, while in Xsum summary tasks (NLU), like hard sequence tagging tasks (QA), prompt tuning may have slightly worse performance compared to fine-tuning. It is important to consider the task requirements and model scale when choosing between these techniques.
3. ptuning v2 实现代码
class RobertaPrefixForTokenClassification(RobertaPreTrainedModel):
# deep prompt tuning
def get_prompt(self, batch_size):
prefix_tokens = self.prefix_tokens.unsqueeze(0).expand(batch_size, -1).to(self.roberta.device)
past_key_values = self.prefix_encoder(prefix_tokens)
past_key_values = past_key_values.view(
batch_size,
self.pre_seq_len,
self.n_layer * 2,
self.n_head,
self.n_embd
)
past_key_values = self.dropout(past_key_values)
past_key_values = past_key_values.permute([2, 0, 3, 1, 4]).split(2)
return past_key_values
# reparameterized encoder(MLP)
class PrefixEncoder(torch.nn.Module):
r'''
The torch.nn model to encode the prefix
Input shape: (batch-size, prefix-length)
Output shape: (batch-size, prefix-length, 2*layers*hidden)
'''
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.prefix_projection = config.prefix_projection
if self.prefix_projection:
# Use a two-layer MLP to encode the prefix
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(config.pre_seq_len, config.hidden_size)
self.trans = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.prefix_hidden_size),
torch.nn.Tanh(),
torch.nn.Linear(config.prefix_hidden_size, config.num_hidden_layers * 2 * config.hidden_size)
)
else:
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(config.pre_seq_len, config.num_hidden_layers * 2 * config.hidden_size)
def forward(self, prefix: torch.Tensor):
if self.prefix_projection:
prefix_tokens = self.embedding(prefix)
past_key_values = self.trans(prefix_tokens)
else:
past_key_values = self.embedding(prefix)
return past_key_values